Does your front end feel vague or flex excessively when you really push it? That "noodle fork" sensation – steering wandering under hard cornering, brake shudder, or a general lack of precision – can be unnerving and slow you down. While some flex is inherent and even desirable for small bump compliance, excessive flex hurts control. Here's how to dial in more stiffness:
1. Increase Air Pressure (Air Forks Only): The simplest and most direct adjustment. Adding air pressure compresses the air spring more, requiring more force to initiate movement. This significantly increases the overall stiffness of the fork, especially resisting large impacts and big compressions that cause flex. Crucially: Stay within the manufacturer's recommended maximum pressure (usually printed on the fork leg). Exceeding it risks seal failure or even catastrophic damage. Start with 5-10 PSI increases, test ride, and repeat cautiously.
2. Add Volume Spacers (Air Forks Only): These small plastic tokens fit inside the air spring chamber. They reduce the air volume. Why does this help stiffness? With less volume, the air pressure ramps up much more aggressively deeper into the fork's travel. This primarily increases mid-to-end stroke support. While not directly stiffening the initial feel like pure pressure, it combats the deep dive that often feels like flex under heavy braking or big G-outs, making the fork feel more supportive and planted overall.
3. Adjust Compression Damping:
- Low-Speed Compression (LSC): Found on most mid-to-high-end forks. This controls the fork's resistance to slow, deliberate movements like braking, cornering, and pedaling forces. Increasing LSC adds significant resistance to these forces, directly combating brake dive and the flex/wander feeling during hard cornering. Turn the dial clockwise (usually) a click or two at a time and test.
- High-Speed Compression (HSC): Less common, controls resistance to sharp, fast impacts (rocks, roots). While primarily for tuning big-hit harshness, a slight increase might offer a subtle perception of firmness, but focus on LSC first for stiffness related to steering inputs.
4. Increase Oil Viscosity (Advanced): Fork oil lubricates and dampens. Thicker oil (higher viscosity, e.g., going from 5wt to 7.5wt or 10wt) creates more resistance inside the damper. This makes the damper cartridge stiffer, particularly the compression circuit, requiring more force to move the fork quickly. This is an advanced modification. Research your specific fork model thoroughly – using oil that's too thick can damage internals, make the fork harsh, and void warranties. Best done during a full service.
5. Service Your Fork: Worn bushings, contaminated oil, or degraded seals introduce slop and reduce the fork's ability to move smoothly in its intended path. This often manifests as play or a vague, "sticky" flex feeling. A full lower leg service (replacing oil, seals, and bushings if needed) restores the fork's tightness and responsiveness, eliminating unwanted movement that feels like flex.
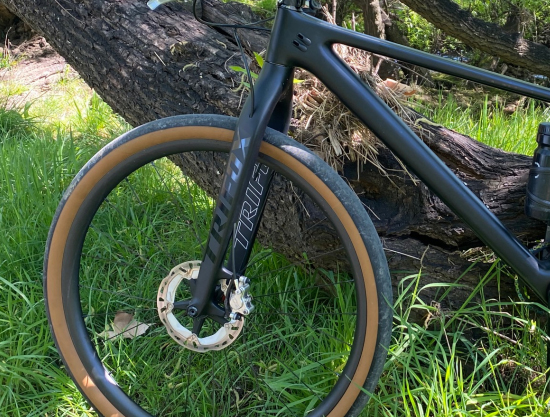

Important Considerations:
- Trial & Error: Stiffness preferences are personal. Make one change at a time and test thoroughly on familiar terrain.
- Trade-offs: Increasing stiffness almost always reduces small-bump sensitivity and plushness. Find the right balance for your riding style and terrain.
- Fork Limits: Every fork has a design stiffness. Aggressive riders on lightweight XC forks will hit limits faster than someone on a burly enduro fork. If you've maxed out adjustments and servicing, a stiffer chassis might be the ultimate solution.
- Headset Check: Ensure your headset is properly preloaded. A loose headset feels like fork flex!
By methodically working through these adjustments – starting with air pressure/volume and compression damping – you can significantly reduce unwanted flex and gain the precise, confident front end your aggressive riding demands.