Today, I will explain the various gripping postures of the road bike handlebars, as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages, so that the rider can master the profound meaning of changing riding postures.
Based on the grip position of a road handlebar, can be easily divided into three types: the hand is placed on the position of the brake shifter、the hands are placed on the upper end of the handlebar、and the hands are grasped on the lower bar.
Regarding these three kinds of handlebar grip positions, in fact, each has its advantages and disadvantages, but more importantly, each kind of bend grip position can allow the rider to better face the special riding road conditions. Of course, the handlebar grip guide discussed below is just a reference. After all, the rider’s riding habits and body feel are also very important, and these factors must be taken into consideration. In this article, we’ll highlight the pros and cons of each grip, as well as the recommended times to use it.
The grip of the brake lever
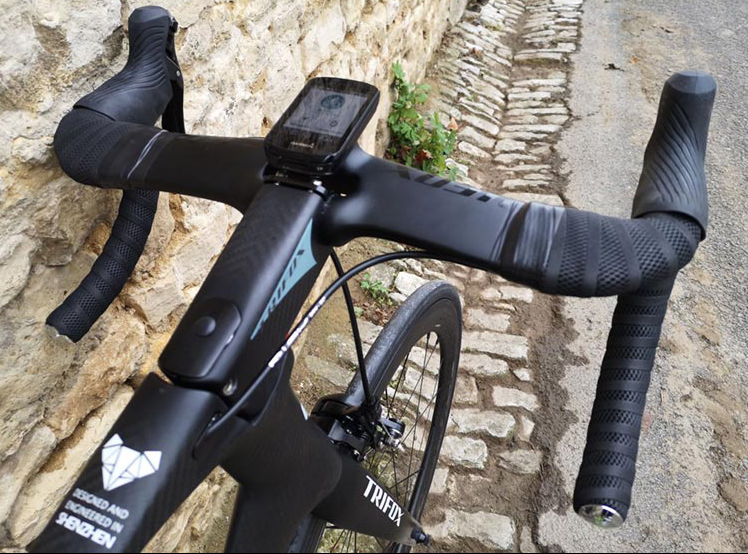

This is the most versatile and common gripping posture for road bikes because this gripping posture can be used for comprehensive terrain types such as uphill, downhill, and flat roads. This kind of braking posture can also strike a balance between aerodynamics and comfort, and more importantly, it has the advantage of being able to control the brake lever at any time. It is recommended that you use this grip during training, whether you are riding alone or in a group. The most important factor is that it can provide a comfortable riding position without affecting safety.
In competitions (including professional competitions), it is also the most common grip position, and it can maintain good comfort even for hours of long-distance riding. In the face of a sudden need to change to a standing posture, in response to acceleration or changes in the terrain, there is no need to change the grip position of the hands when changing the riding posture with the brakes. In addition, if there is no need for ultra-high-speed downhill, this riding posture can also maintain good handling and stability and allows the rider to control the brakes at any time. However, if the rider wants to pursue maximum controllability and braking force, we still suggest that it would be more appropriate to hold both hands on the lower handle.
Top grip position

As the name suggests, put your hands on the flat top of the handlebar. Since this riding position brings the hands closest to the body, it keeps the back more upright for optimized riding comfort. However, the biggest disadvantage is that it will reduce aerodynamics. However, let’s not talk about this riding position may reduce aerodynamics. Since the handling of this riding position is not good, it is not recommended to use it when riding at high speed. The most important factor is that the brake lever cannot be controlled immediately.
Another reason is that since this riding posture will make the holding distance of the hands closer, it will reduce the handling performance, especially in the face of emergency situations, such as sharp turns or obstacles, which are very unfavorable manipulation. For this reason, the suggestion for the use of the upper position is in situations where the brakes are not required, such as when climbing a slope or on a road with few people and vehicles.
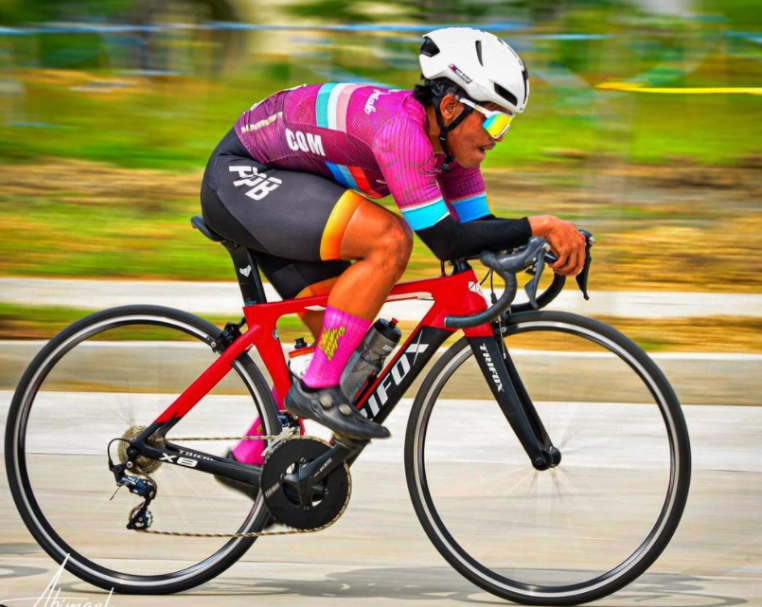
lower grip position
This is the grip position for the best handling. The disadvantage is that its comfort is obviously not as good as the other two riding positions, but it allows both hands to have greater control torque, and it can not only improve aerodynamics but also have very good handling. In addition, the grip position of the lower bar is also easy to operate the brake lever and can get better braking force than using the brake lever position. The recommended time to use it is on difficult stages, such as high-speed sprints and downhills. In these situations, you can see that professional drivers use the lower bar position. By using this kind of bending posture, the angle of the back can be made close to the level, and the aerodynamic advantage can be optimized.